Let’s Talk About Reading
Reading development is a multifaceted process that involves numerous cognitive, linguistic, and environmental factors. Here's a summary of some of the key complexities involved:
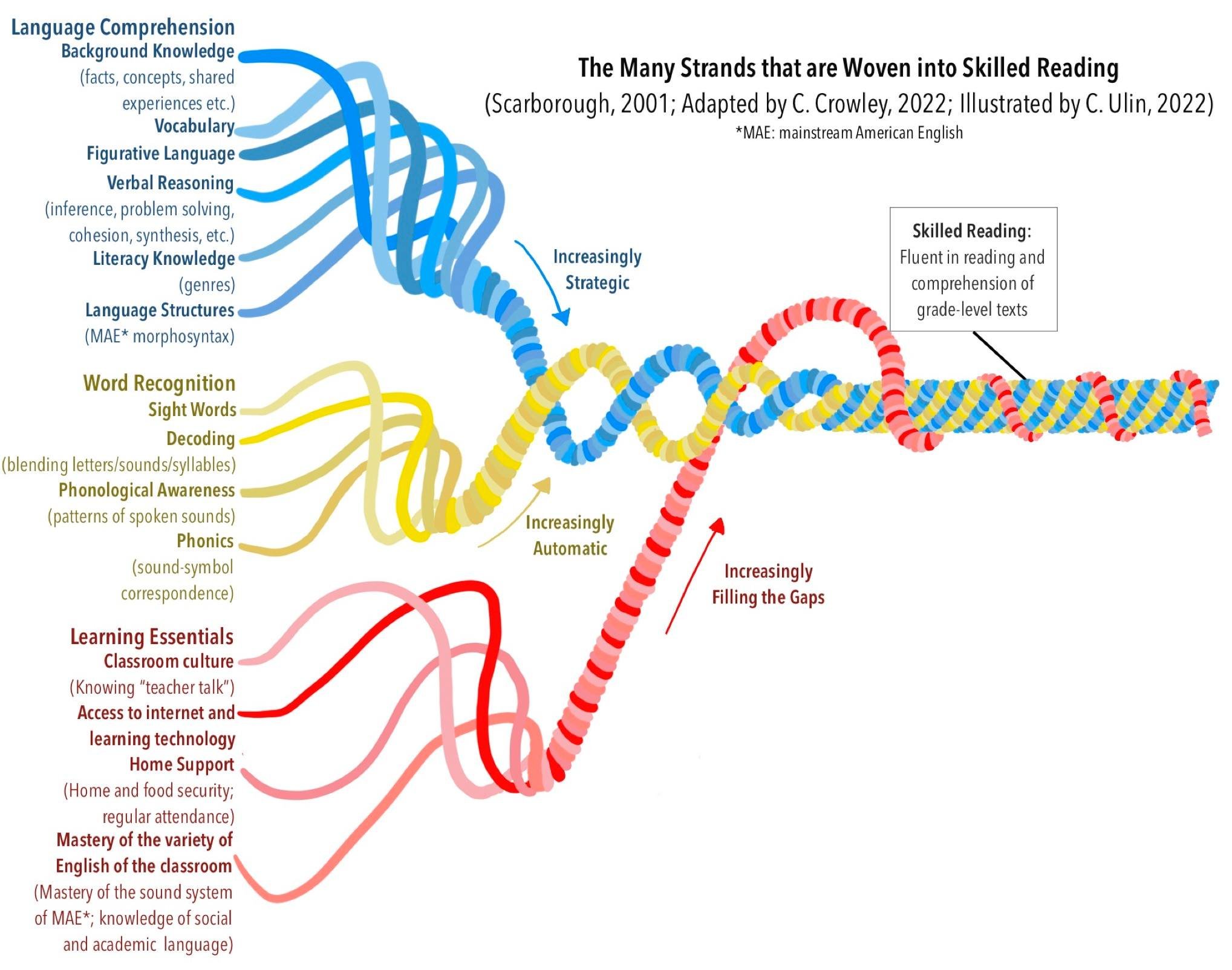
Phonological Awareness: This refers to the ability to recognize and manipulate the sounds of spoken language. Children need to develop phonological awareness to understand the relationship between sounds and letters, which is crucial for decoding words while reading.
Decoding Skills: Decoding involves applying knowledge of letter-sound correspondences to recognize words. This skill develops gradually as children learn the alphabetic principle and phonics rules.
Vocabulary Development: Building a robust vocabulary is essential for reading comprehension. Children must learn the meanings of words and understand how they are used in context.
Comprehension Strategies: Effective readers employ various strategies to understand and remember what they read. These strategies include making predictions, asking questions, summarizing, and making connections to prior knowledge.
Fluency: Fluency refers to the ability to read text accurately, quickly, and with expression. Fluent readers can recognize words automatically, allowing them to focus on comprehension rather than decoding.
Socio-cultural Factors: Socioeconomic status, home literacy environment, and cultural background can significantly influence reading development. Access to books, exposure to rich language, and parental involvement in literacy activities can all impact a child's progress in learning to read.
Individual Differences: Children vary in their learning styles, strengths, and challenges. Some may struggle with specific aspects of reading, such as phonemic awareness or comprehension, while others may excel in these areas. It’s important to emphasize your child’s reading strengths!
Motivation and Engagement: Motivation plays a crucial role in reading development. Children who are motivated to read are more likely to invest time and effort in practicing their reading skills, leading to greater proficiency over time.
Instructional Approaches: Effective reading instruction involves a combination of explicit teaching, guided practice, and opportunities for independent reading. Different instructional approaches, such as phonics-based instruction or whole language approaches, may be more suitable for different learners.
Continued Growth: It’s important to know that reading development is not a linear process but rather a continuous journey that extends throughout a person's lifetime. Even proficient readers continue to refine their skills and expand their literacy abilities through ongoing practice and exposure to diverse texts.
Are you interested in learning more about your child’s reading profile?